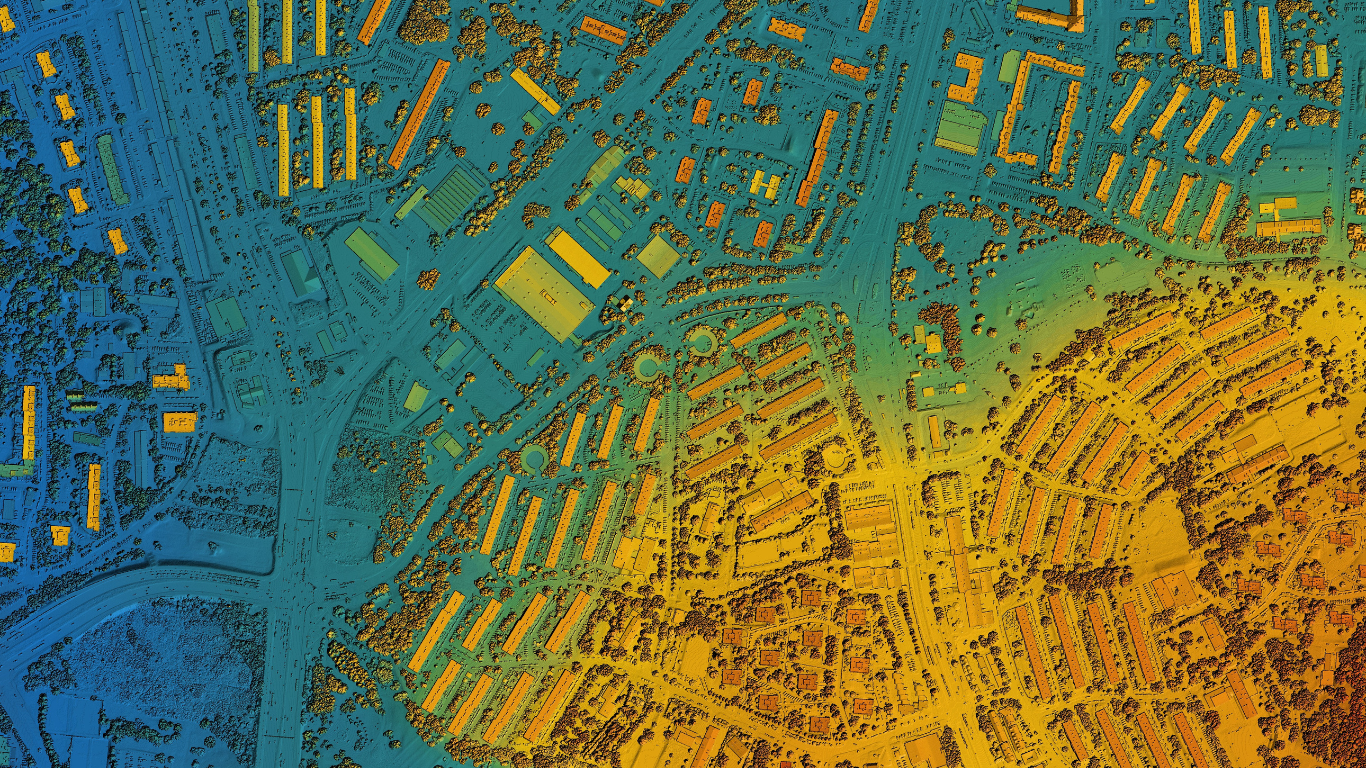
As geospatial technology continues to prove its value to local governments up and down the country, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as an indispensable tool for local councils to communicate data through visual representations. By enabling the interpretation and analysis of data in ways that reveal relationships, patterns, and trends, GIS assists local councils and urban planners in making informed decisions that shape the future of communities. This article explores how UK councils can utilise the power of GIS mapping to enhance community development and improve public services.
Understanding GIS Mapping
In its simplest form, Geographic Information System Mapping – or GIS mapping – is an innovative technology that combines cartographic science with GPS data to collect, manipulate, analyse, and present all types of interactive geographical data.
For example, a basic map could show the streets of a city. A GIS map, however, can integrate various data layers like the location of schools, parks, hospitals, or even traffic density patterns at different times of the day. This intersection of geography and data provides a powerful platform for decision-making and policy development, serving as critical tools in urban planning, resource management, and public service delivery.
An impressive example of the capabilities and information available with GIS technology is The Greater Manchester Open Data Infrastructure Map (GMODIN), this interactive, free-to-use map layers multiple datasets across a variety of topics — from environmental assets to energy utility networks.
Applications of GIS in Community Development
Urban Planning and Zoning:
By analysing GIS mapping, local councils can overlay different data sets to see how various elements of a city interact. This allows for data-driven spatial analysis and modelling during planning stages, identifying the best sites for new housing developments, public facilities, and green spaces. GIS aids planners in generating precise population forecasts, evaluating the influence of new developments on traffic flow, and making better-informed choices regarding the distribution of new public amenities.
Furthermore, GIS allows for ongoing evaluation, monitoring, and feedback, making it an indispensable tool for continuously adapting and improving urban plans. This level of detailed spatial analysis and visualisation is essential for effective urban planning reform.
Environmental Management and Conservation:
Environmental conservation and management are other crucial areas where GIS mapping has proven invaluable to local councils. By mapping areas of ecological significance, such as wetlands, forests, and AONBs, councils can map and track the impact of human activities on natural landscapes, enabling targeted conservation efforts and sustainable management practices. For instance, GIS can help identify regions prone to erosion or flooding, allowing for proactive measures to protect communities and ecosystems.
Transportation and Public Services:
GIS assists in designing efficient transportation networks and infrastructure. By analysing traffic patterns, population density, and existing road networks, councils can plan and prioritise road improvements, public transport routes, and waste collection routes. GIS data also supports the maintenance and management of infrastructure like water supply, sewer systems, and electrical grids.
This level of planning efficiency is crucial for the delivery of high-quality public services that meet the ever increasing needs of the community and fosters a sense of care and accountability among the public towards government departments.
Public Safety and Emergency Response:
In times of emergency, GIS provides the relevant emergency services with the information necessary for greater situational awareness, more effective communication and quicker, more impactful responses. GIS can create real-time maps and spatial models containing important information like evacuation routes, flood zones, and critical infrastructure locations, which can help emergency management departments to prepare for and react to disasters and emergencies quickly and effectively.
For public safety, GIS supports crime analysis and prevention by identifying crime hotspots and allocating preventative measures. Mapping crime data for instance, helps allocate resources where they are needed most. During emergency responses, GPS data can be crucial for real-time decision-making and accurate resource allocation.
Conclusion
GIS technology serves as a transformative force for local government departments. Equipped with the appropriate tools and resources, local governments are empowered to make swift, well-informed decisions, elevate the quality of their services, and foster improved communities for their citizens.
The integration of GIS in local governance signifies a leap towards more transparent, efficient, and community-focused urban development. By continuing to harness the potential of GIS mapping software, local councils can effectively navigate the complexities of urban planning, ensuring the well-being and sustainability of the communities they serve.
Place Informatics is a leader in GIS mapping technology with experience in urban planning and community development. Having worked alongside numerous local councils, we understand how GIS can be effectively utilised for strategic planning. For more information on how we can help your organisation, contact Place Informatics at 0161 706 1343 or schedule a discussion by clicking the booking link below.
https://calendly.com/clive-hall/diary-booking